Warehouse Safety – The safety master

Reasons You Should Conduct Regular Safety Audits
May 2, 2022
What is HAZOP? Hazard and Operability Study
May 7, 2022A warehouse could be a building for storing goods. Warehouses are utilized by manufacturers, importers/exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, etc. they’re usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities, towns, or villages.
They generally have loading docks to load and unload goods from trucks. Sometimes warehouses are designed for the loading and unloading of products directly from railways, airports, or seaports. They need cranes and forklifts for moving goods, which are usually placed on ISO standard pallets so loaded into pallet racks. Stored goods can comprise raw materials, packing materials, spare parts, components, or finished goods associated with agriculture, manufacturing, and production. In India, a warehouse could even be said as a “go down”
Warehousing vs. Storage
The semantic distinction between warehousing and storage is ambiguous. Yes, warehouses are for storage, but they are stored with the intention of selling, and most warehouses are high-volume, fast-paced environments where goods are continually moved.
Storage typically refers to the safekeeping of non-commercial assets and liabilities. Consider a storage unit. People put everything that won’t fit in their garage into their storage unit because their garage is already crowded with other stored items, all of which are likely to be retained for a long time.
Warehouse Safety
Warehouse safety could be a set of regulatory guidelines and industry best practices to assist warehousing employees to ensure a secure work environment and strengthen safe behavior when working in warehouses. For sustainable warehouse operations, health and safety should be prioritized because the fatal injury rate for the warehousing industry is above the national average for all industries
Warehouses are dangerous places to figure in, it’s important to grasp common warehouse dangers and hazards because they will cause injuries and in extreme cases death
Regulations and Standards
Hazard Communication
Warehouse operators should prepare and execute a written Hazard Communication program and warehouse workers who could also be exposed to hazardous chemicals.
Emergency Action Plan (EAP)
If warehouse owners don’t have an in-house fire brigade, then they ought to have an in-depth plan Describing the actions warehousing employees should soak up in the event of a hearth or other emergency situations.
Fire Safety
Warehouse management employing over 10 workers should have a written fire prevention plan,
Exit Routes
Warehouses should have a minimum of two well-designed and constructed fire escape routes located as remote as practical from one another just in case one is blocked by fire or smoke.
Walking / Working Surfaces
Warehouse and storage facility workers engage at heights, especially on elevated platforms. Should have fall protection systems to shield themselves from falls
Medical and attention
Warehouse operators supply medical and first-aid personnel and supplies commensurate with warehouse hazards like faulty pallet racks and racking falls thanks to unsafe use of forklifts, among others.
Hazard and Control
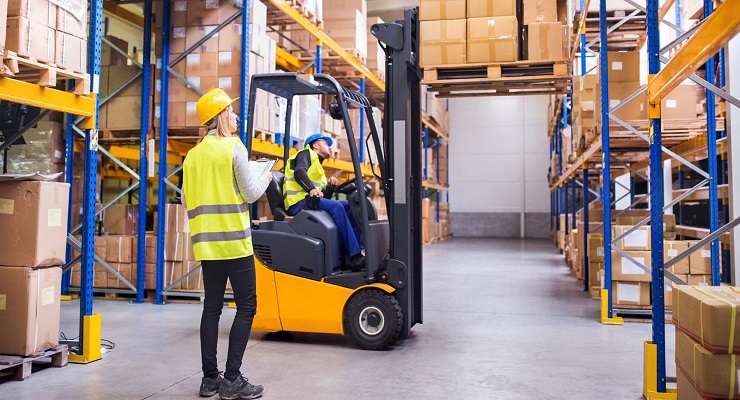
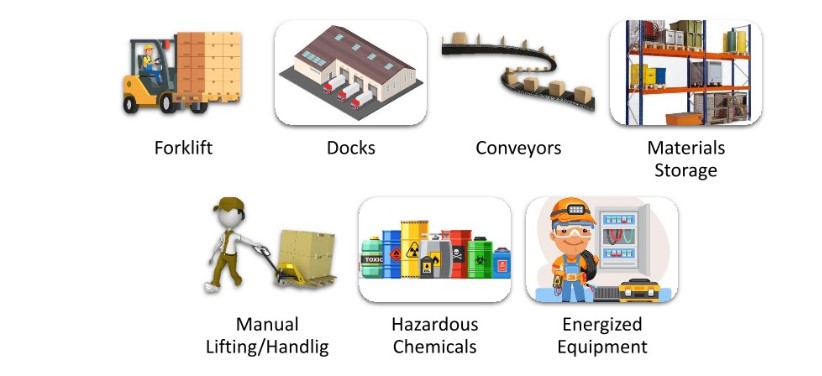
1. Forklifts are critical pieces of equipment used in warehousing and storage facilities. However, when operated incorrectly can cause serious damage to operators, nearby workers, and property. a. Ensure all forklift operators are competent and have completed certified training. Perform
Regular refresher training and evaluation when an operator is observed operating the vehicle in an unsafe manner. b. Perform daily pre-start forklift equipment inspections to check for controls and equipment damage.
2. Docks-One of the worst accidents a worker could suffer when working in a warehouse is being pinned or crushed between a forklift truck and the loading dock.
a. Forklift operators must be attentive and drive slowly on dock plates, making sure dock edges are clear and safe to support loads.
b. Always ensure that warning signs and mechanisms are in place to prevent people from getting near docks.
3. Conveyor equipment is usually utilized in the transportation of products from warehouse to warehouse. However, conveyors pose serious dangers to workers including getting caught in equipment and being struck by falling objects.
a. Ensure proper safeguarding equipment between the conveyor and also the worker to guard against the entanglement of clothing, body parts, and hair.
b. Follow proper lockout tag-out procedures during conveyor maintenance and repairs
4. Materials storage – Improper stacking of loads and storage of materials on shelves may result in unintended slip and trip hazards for nearby workers. a. Keep aisles and passageways clear and in condition, this prevents workers from slipping, tripping, or falling.
b. Loads should be placed evenly and properly positioned, heavier loads must be stacked on lower or middle shelves. Always remember to get rid of one load at a time.
5. Manual lifting/handling- the foremost common explanation for physical injuries in warehouse and storage facilities involves improper manual lifting and handling. Failure to follow proper procedures can cause musculoskeletal disorders, especially if finished awkward postures.
a. Plan ahead and determine if the requirement for lifting is often minimized by applying good engineering design techniques.
b. Observe proper ergonomic posture when carrying or moving loads. If products are too heavy, ask assistance from a co-worker. Learn more about the principles of ergonomics within the workplace.
6. Hazardous chemicals – when handling hazardous chemicals in your warehouse or storage facilities, a hazard communication program should be implemented. Your hazard communication program should cover effective training on identifying chemical hazards, proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals; and also the use of appropriate PPE (personal protective equipment).
7. Energized equipment A Lockout/tag-out (LOTO) program must be implemented altogether in warehouse operations to make sure that each energized equipment is correctly shut off and to stop employees from being caught between mechanical parts or being electrocuted. All affected workers must be trained on LOTO procedures and the way to use and take away LOTO devices after performing maintenance to confirm warehouse safety.
Send us your inquiry to info@thesafetymaster.com or speak to our expert at +917665231743 for getting the above services today to achieve safety goals.




